What is Domain Name? (The Best Guide to Know About Domains)
In today’s world, everyone knows what is domain name. But I wanted to cover this topic in a lot more detail than just some general things. So, let us get into it straight.
Domain name is a web address consisting of a website name and its extension (.com, .net, .org. etc.). The name is up to you – as long as it consists of letters, numbers, hyphens and is still available, whereas the domain extension is usually a set combination of a few letters.
Just like a physical address helps people find a specific place, the purpose of a domain is to help visitors find a website. Without it, users can only access websites using Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. These IP addresses are assigned by the domain name registrar. Additionally, domain name registrar also handles the reservation of domain names. It is simpler to access websites without having to memorise and type in numeric IP addresses by selecting a reliable domain name and registrar. Check out our detailed guide on how to choose best domain registrar for your website.
However, IP addresses are hard to remember as they consist of random series of numbers, making them inconvenient to share. Domain names, on the contrary, can help drive traffic to your website.
In this article, we will cover all the necessary information about domain names. We will explain how domains work and their different types. Then, we will show how to register, transfer it and answer some frequently asked questions.
How Do Domains Work?
Every website has the following two main elements: a domain name and a web hosting server. Your domain name is built on the web hosting server. For more in-depth knowledge on what exactly is domain and what exactly is a web hosting server, check out our detailed guide on what Is The Difference Between Domain Name And Web Hosting. If you are a beginner and are confused to choose the correct WordPress host, check out our guide on how to choose best WordPress hosting.
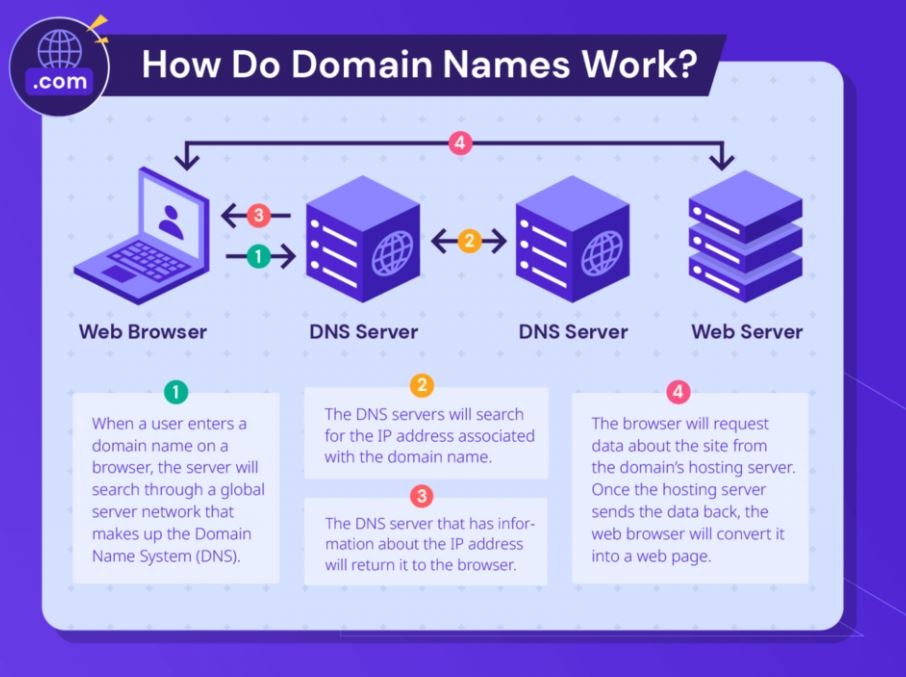
Keep note that every domain is linked to an IP address. When a user enters a domain name into a web browser (say Google Chrome), the server will then perform a search through a global server network. The DNS servers will search for the IP address associated with it. The server that has information about the IP address will return it to the web browser. Then, it will request data about the site from the domain’s hosting server.
The web server stores all of the website data, including the number of web pages it has, text, images, videos on the pages, and much more. Once the hosting server sends the data back, the web browser will convert it into a web page that users can visit.
Types of Domains
Here are some of the most common types of domains that exist:
Top-Level Domains (TLD)
A top-level domain is a domain name extension. Various TLDs are available online, but .com is the most popular extension, with over 52% of all websites having it. Using a more popular extension drives higher organic traffic as users often write it by default.
However, using a less popular extension, such as .online, often costs less and can make a domain more unique. With the increasing number of new websites created daily, the popularity of a specific TLD might also change in the future.
Check out the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) for the official list of all legitimate TLDs.
Country-Code Top-Level Domains (ccTLD)
A country-code top-level domain is an extension that is specific to a particular country. It consists of two letters based on the international country codes (.in, .us, .eu, and more).
There are platforms that help find the correct country codes, such as the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)’s database. To illustrate, sites from Japan can use .jp as their extensions, whereas Brazilian sites use .br.
A ccTLD is useful for a company that focuses on a specific country. This way, international companies can differentiate their content for different regions.
For example, the BBC uses bbc.co.uk to target readers in the United Kingdom, and bbc.com for the international audience.
Generic Top Level Domains (gTLD)
A generic top-level domain is an extension that does not rely on a country code. There are no specific criteria to get a gTLD. However, some extensions are sponsored by designated agencies or organizations.
Some generic TLDs are restricted to specific types of registrants. For example, an academic institution can use .edu, and a governmental agency can use .gov. If your domain does not fall under particular categories or institutions, you will not be able to use the extension.
Other Domain Name Types
We focused on the different extension types above. The following are the different available structures of domain names:
Second-Level Domains
Second-level domains (SLDs) are below TLDs in the domain name hierarchy. An SLD is the section of a domain name located on the left side of the last dot. Take www.reviewsnguides.com, for example – Reviews N Guides is the SLD, and .com is the TLD.
Some registries use an SLD to indicate a specific type of entity registering. For example, academic institutions in the United Kingdom mostly register websites under .ac.uk.
Subdomains
A subdomain is a spin-off from the main domain and shares the same servers. For example, Google uses developers.google.com to provide specific information for developers. There is no need to purchase and register a subdomain.
The most common use for a subdomain is to organize and divide web content into separate sections.
Another use of a subdomain is to create another website with the same name but different languages. Take Wikipedia as an example, which has a separate subdomain for each language. It uses en.wikipedia.org for the English version and es.wikipedia.org for the Spanish one.
Free Domains
Website builders, such as WordPress.com, or content management systems, like WordPress, often offer free domain names for new users. Usually, beginners take this opportunity to create their websites before investing money into them.
Keep in mind that getting a free domain often comes with minimal features and tools.
Why Do You Need Domain Name?
if you want to make your own website, you’ll need a domain name so that other people can visit your website from their computers.
People want to start websites for a number of different reasons, which is why there are millions of registered domain names. Here’s why you should consider:
- Domain Name Is unique and searchable
- Domain Name has authority
- You control your Domain
Difference Between Domain Name & URL
Though they might look almost the same, a domain name and URL are 2 different things. Domain name hosts the complete website, including multiple URLs or web pages of that website. For example, it is the actual name of the website like reviewnguides.com, whereas a URL is the entire path of a website that leads you to a particular page like https://reviewsnguides.com/guides/. Basically, the URL is the complete internet address used to locate a specific page and it includes the domain name.
The URL (Uniform Resource Locator) instructs your browser exactly where to go using a specific protocol which is most commonly the HTTP or HTTPS part of a URL. Then the last part of the URL directs your browser on which page of a website to go to, like the guides page.
How to Choose Good Domain Name?
Choosing the right domain name for your website is important. It’s not a decision you should make hastily, you need to really think about it and come up with a domain name that’s unique, memorable, and one that works for your website.
There are a number of tips you should remember when choosing a domain name including:
- Keep it Short – Don’t make your domain too long, it will be harder for people to remember and more difficult to spell. Spelling errors can cause your website a loss of traffic.
- Stick with .com – The domain extension .com is the most popular and trusted, so stick with it.
- Use Keywords – Keywords will help search engines determine what your website is all about and make it easier for users to find you online. So if you’re a photography website, use the keyword “photography” in your domain name.
- Avoid Numbers & Hyphens – Numbers can lead to misspellings of your domain name, like “five” instead of “5”. And hyphens are often used by spam sites, which you don’t want to be associated with
How to Register Domain Name?
Getting your own domain name isn’t difficult. You can register and purchase a it from many different companies. Typically it costs around $14.99/year from popular companies like GoDaddy, BlueHost, Hostinger, and Namecheap.
Summing Up
In this article, we have discussed all the necessary information on domains. Most importantly, we have explained why a domain name is essential for your website.
Here’s a recap of how domains work:
- You enter a domain name into a web browser.
- The DNS servers look for the website’s IP address.
- The browser asks the server for the site’s data.
- The browser displays the website.
There are different types of domains available, categorized by extension and structure types. Once you have a domain in mind, we have shared the steps to register it.
Now that you know all of this, go ahead and register domain yourself.

Leave a Reply